Thermoacoustic Instability
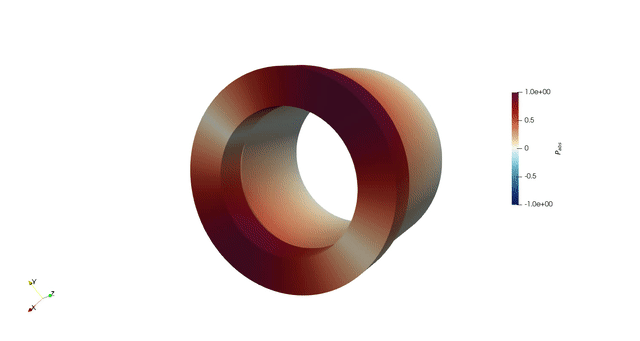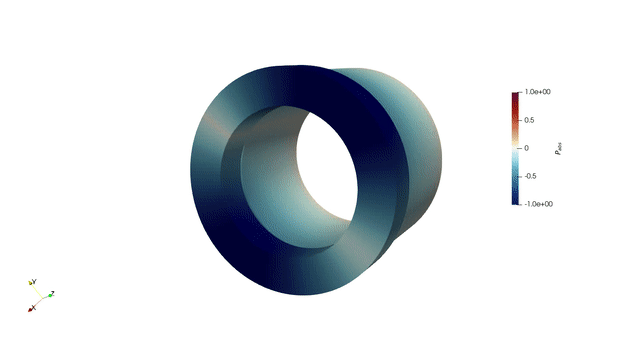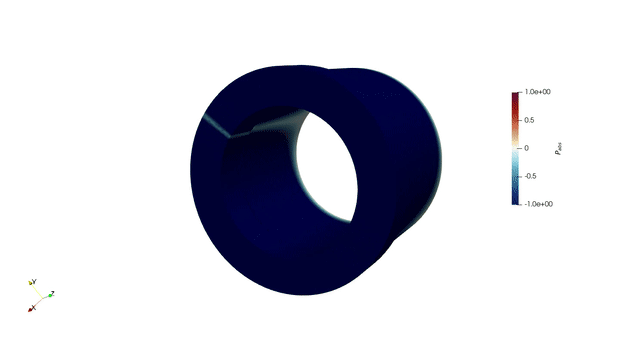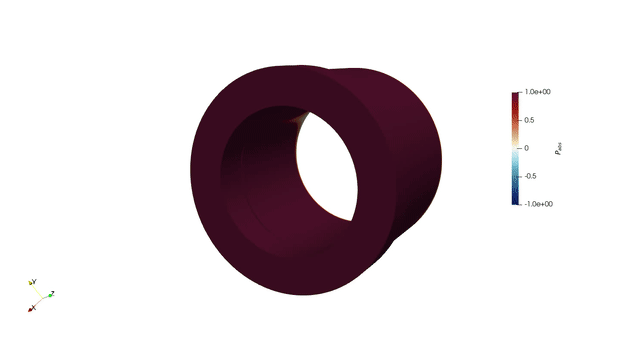
Overview
Thermoacoustic instability occurs in gas turbine combustors due to the dynamic coupling between heat release rate and acoustic oscillations. If the unsteady heat release rate is sufficiently in phase with the acoustic pressure, then the amplitude of the acoustic pressure intensifies. This increases the fatigue of the components and can lead to engine failure. Frameworks that offer quick and accurate results to study thermoacoustic instability are desirable, since the system’s stability is extremely sensitive to small changes.
In my PhD, we developed a 3D thermoacoustic Helmholtz solver, helmholtz-x. This framework simulates the thermoacoustic behaviour of increasingly complex geometries and suggests design changes through adjoint methods combined with geometry parametrization techniques: NURBS and Free Form Deformation. We used adjoint methods to accelerate optimization process. We greatly benefitted from finite element method (FEM) to handle complex combustor geometries.
